INTRODUCTION: Ketosis is a physiological state of the body which occurs when the reduction of carbohydrates forces to burn fatty acids to provide energy, as ketone bodies.
Ketogenic diets include dietary treatments with a reduction of intake of carbohydrates (usually less than 50 g/die) and a relative percentage increase in fat and protein.
Very Low Calorie Ketogenic Diet (VLCKD) with amino acid supplementation is associated with a weight loss at the only expense of the Fat Mass, preserving Free Fat Mass, when compared with a diet restricted in calories but not ketogenic.
Even on long term, VLCKD is significantly more effective in maintaining the weight loss compared with standard low calorie diet in obese patients.
VLCKD has proved to be an effective treatment because the only Fat Mass is reduced, with no changes in the resting metabolic rate.
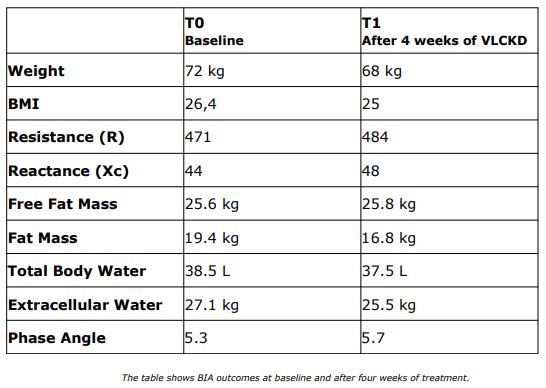
OBJECTIVE: Weight regain is the most common consequence of dieting therefore weight loss should be strictly associated with Fat Mass loss and with the preservation of the Free Fat Mass. The aim of the case report is to evaluate the effectiveness of a VLCKD with protein replacement to preserve lean mass.
PATIENT AND METHODS: Our patient was a 44-years old woman seeking body reshape after pregnancy. We analyzed patient blood test, collected anthropometrics measurements and bioelectrical impedance (BIA) was performed. Patient followed a VLCKD with protein replacement for four weeks.
RESULTS: After four weeks of treatment, patient lost more than 5% of body weight, exclusively in Fat Mass and extracellular water. All body circumferences and Body Mass Index (BMI) were improved.
CONCLUSIONS: The case report demonstrates the efficacy of the VLCKD in Fat Mass loss and body reshape.
Protein replacement is useful to ensure the correct protein intake to preserve lean mass.
https://www.aestheticmedicinejournal.org/?wpdmpro=amj-april-
Paoli A, Rubini A, Volek JS, Grimaldi KA. Beyond weight loss: a review of the therapeutic uses of very-low-carbohydrate (ketogenic) diets. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2013 Aug, 67(8): 789–796.
Merra G, Miranda R, Barrucco S, Gualtieri P, Mazza M, Moriconi E, Marchetti M, Chang TF, De Lorenzo A, Di Renzo L. Very-low-calorie ketogenic diet with aminoacid supplement versus very low restrictedcalorie diet for preserving muscle mass during weight loss: a pilot double-blind study. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2016 Jul, 20(12):2613-21.
Moreno B, Bellido D, Sajoux I, Goday A, Saavedra D, Crujeiras AB, Casanueva FF. Comparison of a very low-calorie-ketogenic diet with a standard low-calorie diet in the treatment of obesity. Endocrine. 2014 Dec, 47(3):793-805.
Moreno B, Crujeiras AB, Bellido D, Sajoux I, Casanueva FF. Obesity treatment by very low-calorie-ketogenic diet at two years: reduction in visceral fat and on the burden of disease. Endocrine. 2016 Dec, 54(3):681-690.
Gomez-Arbelaez D, Crujeiras AB, Castro AI, Martinez-Olmos MA, Canton A, Ordoñez-Mayan L, Sajoux I, Galban C, Bellido D, Casanueva FF. Resting metabolic rate of obese patients under very low calorie ketogenic diet. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2018 Feb, 17;15:18.
Krebs, H.A. The regulation of the release of ketone bodies by the liver. Advances in Enzyme Regulation. 1966, Vol. 4, 4:339–354.
RL., Veech. The therapeutic implications of ketone bodies: the effects of ketone bodies in pathological conditions: ketosis, ketogenic diet, redox states, insulin resistance, and mitochondrial metabolism.
Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2004 Mar, 70(3):309-19.

